Long term outcomes of posterior leaflet folding valvuloplasty for mitral valve regurgitation
Abstract
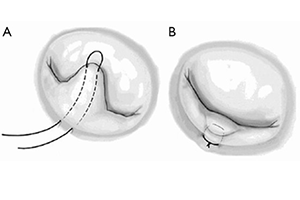
Background: Posterior mitral valve leaflet prolapse due to degenerative mitral valve disease has been treated with tissue sparing repair techniques since 2002. The simplified foldoplasty technique effectively lowers the height of the redundant posterior leaflet and creates an optimal coaptation line for the anterior leaflet that results in excellent long term durability, freedom from reoperation, and return of functional status.
Methods: Patient demographics and in-hospital outcome data were extracted from electronic medical records of 229 patients, aged 60.6±13.7 years who underwent the procedure for mitral valve repair (MVR) involving the posterior leaflet from myxomatous disease between 2002 and 2014. Parametric analyses were performed on outcomes data, while long-term survival was assessed by Kaplan-Meier analyses.
Results: Concomitant coronary bypass surgery was performed on 32/229 (14%) patients, the mean perfusion time was 119±40 min, and the mean cross clamp time was 86±31 min. Post-operative mortality was 2/229 (0.9%), reoperation for bleeding occurred in 4 (1.7%) and postoperative stroke in 4 (1.7%) patients. Long term follow up rate was 100% and the mean study follow-up duration was 6.8±2.3 years. Overall late mortality rate was 24/229 (14.9%), and mitral valve re-intervention was performed on 7 patients (4.3%). NYHA class III/IV and clinically significant MR at follow up were significantly lower compared to preoperative values (both P<0.001).
Conclusions: Our results encourage further use of this simple and effective technique in patients with isolated posterior leaflet prolapse.
Cover