Durability of continuous-flow left ventricular assist devices: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) are becoming an increasingly viable alternative therapy for heart failure, either as a bridge to heart transplantation (BTT) or destination therapy (DT). The latter has become increasingly popular in recent years, in the face of a donor organ shortage and a rise in elderly patients ineligible for heart transplants. For these patients in particular, device durability is a key contributor to survival, morbidity, and quality of life. This systematic review aimed to assess the long-term durability of current continuous-flow LVADs.
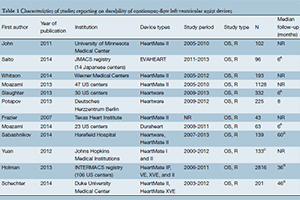
Methods: Six electronic databases were searched from their dates of inception to August 2014 for original studies reporting on patients receiving continuous-flow LVADs. LVAD failure was defined as device malfunction necessitating exchange or explantation, or causing patient mortality. Pooled averages were calculated for outcomes and rates of device failure were reconstructed from digitized graph curves using the software, WebPlotDigitizer v3.3.
Results: Twelve retrospective observational studies with a total of 5,471 patients were included for analysis. The mean duration of LVAD support was 504.7 (range, 303-568) days, and the overall weighted incidence of device failure was 3.9% (range, 1-11.3%). On average, pump thrombosis was the most common cause of device failure (50.5%), followed by lead or cable damage (21.7%), mechanical pump failure (11.6%), devicerelated infection (11.1%), and surgical complications from implantation (2.5%). Long-term device failure rates at 2-, 6-, 12-, 18- and 24-months post-implantation were 0.5%, 1.8%, 2.9%, 4.5% and 6.5%, respectively.
Conclusions: With the expected rise in LVAD usage for end-stage heart failure, particularly as a DT, the steady minority of patients experiencing device failure is likely to increase. Further investigation is required into the incidence and mechanism of major causes of failure, as well as design improvements that may address these complications. There is currently a lack of guidelines and large randomized studies reporting on the aetiology and outcomes of LVAD failure.
Cover