Meta-analysis of intentional sublobar resections versus lobectomy for early stage non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Surgical resection is the preferred treatment modality for eligible candidates with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the selection of sublobar resection versus lobectomy for early-stage NSCLC remains controversial. Previous meta-analyses comparing these two procedures presented data without considering the significant differences in the patient selection processes in individual studies. The present study aimed to compare the overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) outcomes of patients who underwent sublobar resections who were also eligible for lobectomy procedures with those who underwent lobectomy.
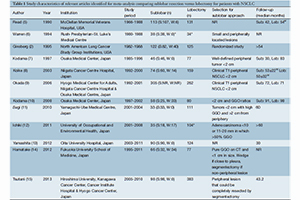
Methods: An electronic search was conducted using five online databases from their dates of inception to December 2013. Studies were selected according to predefined inclusion criteria and meta-analyzed using hazard ratio (HR) calculations.
Results: Twelve studies met the selection criteria, including 1,078 patients who underwent sublobar resections and 1,667 patients who underwent lobectomies. From the available data, there was no significant differences in OS [HR 0.91; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.64-1.29] or DFS (HR 0.82; 95% CI 0.60-1.12) between the two treatment arms. In addition, no significant OS difference was detected for patients who underwent segmentectomies compared to lobectomies (HR 1.04; 95% CI 0.66-1.63, P=0.86).
Conclusions: Using the available data in the current literature, patients who underwent sublobar resection for small, peripheral NSCLC after intentional selection rather than ineligibility for greater resections achieved similar long-term survival outcomes as those who underwent lobectomies. However, patients included for the present meta-analysis were a highly selected cohort and these results should be interpreted with caution. The importance of the patient selection process in individual studies must be acknowledged to avoid conflicting outcomes in future meta-analyses.
Cover