Continuous-flow left ventricular assist device versus orthotopic heart transplantation in adults with heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Due to the lack of donor hearts, many studies have assessed the prognosis of heart failure (HF) patients treated with a continuous-flow left ventricular assist device (CF-LVAD). However, previous results have not been consistent and minimal data is available regarding long-term outcomes. There is no consensus on whether CF-LVAD as a bridge or destination therapy (DT) can equal orthotopic heart transplantation (HTx). The purpose of our study is to compare clinical outcomes between CF-LVAD and HTx in adults.
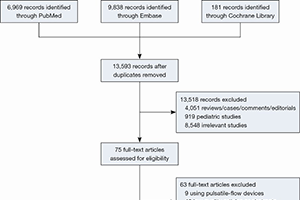
Methods: We searched controlled trials from PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Embase databases until July 1, 2020. The mortality at different time points and adverse events were analyzed among 12 included studies.
Results: No significant differences were found in mortality at one-year [odds ratio (OR) =1.08; 95% CI: 0.97–1.21], two-year (OR =1.01; 95% CI: 0.91–1.12), three-year (OR =1.02; 95% CI: 0.69–1.51), and five-year (OR =1.02; 95% CI: 0.93–1.11), as well as the comparison of stroke, bleeding, and infection between CF-LVAD as a bridge versus HTx. The pooled analysis of one-year mortality (OR =2.76; 95% CI: 0.38–20.18) and two-year mortality (OR =1.64; 95% CI: 0.22–12.23) revealed no significant difference between CF-LVAD DT and HTx. Comparisons of adverse events showed no differences in bleeding or infection, but a higher risk of stroke (OR =5.09; 95% CI: 1.74–14.84) for patients treated with CF-LVAD DT than with HTx.
Conclusions: CF-LVAD as a bridge results in similar outcomes as HTx within five years. CF-LVAD as a DT is associated with similar one-year and two-year mortality, but carries a higher risk of stroke, as compared with HTx.
Cover