Management of retrograde type A IMH with acute arch tear/type B dissection
Abstract
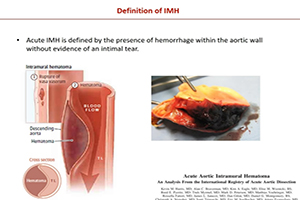
The incidence of intramural hematomas (IMH) in acute dissection (AD) patients varies between 6% and 30% in the literature, most frequently involving only the descending aorta (58%) than the arch or ascending aorta (42%). In this setting, IMH that initiate in the descending aorta, but extend into the arch or ascending aorta have been described, and referred to as a retrograde type A IMH. In these patients the risk of neurological or cardiac complications are high, and therefore an open surgical or hybrid approach has been proposed as the most appropriate. Nevertheless, the endovascular management of such lesions in surgically unfit patients for open surgery have been offered with acceptable outcomes, although the risk of landing in an unsuitable proximal landing zone is evident. In conclusion, retro-TAIMH is an acute aortic syndrome and should be managed as such. The recommended treatment strategy is open surgery for treating ascending or arch involvement, and TEVAR/medical, based on a complication-specific approach, for those with only descending localization. In those patients in whom retro-TAIMH is associated with an acute B dissection presenting with a proximal entry tear located into the descending aorta, a TEVAR represents an option treatment.
Cover