Article Abstract
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in children
Abstract
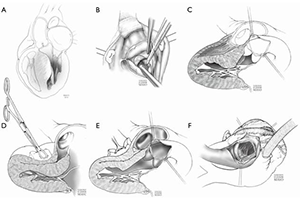
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) occurs in 1 of 500 adults and is considered to be one of the most common causes of death in young people under 35 years of age. Children with HCM are usually asymptomatic and the overall annual mortality beyond the first year of life is 1%. Septal myectomy is safe and effective in children with obstructive HCM and published data shows improved late survival compared to untreated HCM. Patient selection and surgical expertise remain critical components to ensuring successful outcomes of septal myectomy, particularly when considering prophylactic myectomy in a seemingly asymptomatic patient.
Cover