Robotic cardiac surgery in Brazil
Abstract
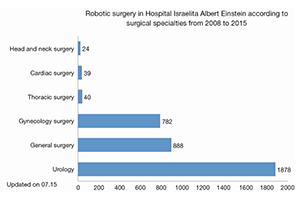
Background: Brazil, the largest country and economy in South America, is a major driving force behind the development of new medical technologies in the region. Robotic cardiac surgery (RCS) has been evolving rapidly since 2010, when the first surgery using the DaVinci® robotic system was performed in Latin America. The aim of this article is to evaluate short and mid-term results in patients undergoing robotic cardiac surgery in Brazil.
Methods: From March 2010 to December 2015, 39 consecutive patients underwent robotic cardiac surgery. Twenty-seven patients were male (69.2%), with the mean age of 51.3±17.9 years. Participants had a mean ejection fraction of 62±5%. The procedures included in this study were mitral valve surgery, surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation, atrial septal defect closure, resection of intra-cardiac tumors, totally endoscopic coronary artery bypass and pericardiectomy.
Results: The mean time spent on cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) during RCS was 154.9±94.2 minutes and the mean aortic cross-clamp time was 114.48±75.66 minutes. Thirty-two patients (82%) were extubated in the operating room immediately after surgery. The median intensive care unit (ICU) length of stay was 1 day (ranging from 0 to 25) and the median hospital length of stay was 5 days (ranging from 3 to 25). For each type of procedure, endpoints were individually reported. There were no conversions to sternotomy and no intra-operative complications. Patient follow-up was complete in 100% of the participants, with two early deaths unrelated to the procedures and no re-operations at mid-term.
Conclusions: Despite the heterogeneity of this series, RCS appears to be feasible, safe and effective when used for the correction of various intra- and extra-cardiac pathologies. Adopting the robotic system has been a challenge in Brazil, where its limited clinical application may be related to the lack of specific training and the high cost of technology.
Cover