Long-term results after robotically assisted coronary bypass surgery
Abstract
Background: Robotically-assisted coronary bypass grafting (CABG) was introduced in 1998 and dedicated centers have continuously applied and developed this minimally invasive method of coronary bypass surgery. While short-term results are relatively well published, data on long-term outcome are limited. In this literature review, we assessed the outcomes after robotic CABG following the first postoperative year.
Methods: We searched PubMed for articles containing the terms “robotic” or “robotically assisted” and “coronary bypass”. A total of 11 papers contained long-term results. We specifically investigated survival, graft patency, freedom from angina and re-intervention, as well as freedom from major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE).
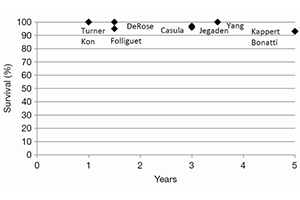
Results: Five-year survival after robotic CABG was consistently consistently greater than 90% and graft patency between 3 and 5 years was reported to be above 90%. Fifteen percent to 26% of patients re-experienced angina at 3 to 5 years postoperatively. Long-term freedom from re-intervention reached the range and the 5-year freedom from MACCE rate was approximately 75%.
Conclusions: According to data in the literature, long-term results after CABG carried out with the assistance of a surgical robot appear to be in line with results achieved after conventional CABG.
Cover